- Queue is implemented using SLL (Singly Linked List ) node.
- Enqueue operation is performed at the end of the Linked list and DeQueue operation is performed at the front of the Linked list.
- With Linked List implementation, for Empty queue
Front = NULL & Rear = NULL
Declaration for Linked List Implementation of Queue ADT
struct node;
typedef struct node * Queue; typedef struct node * position; int IsEmpty (Queue Q); Queue CreateQueue (void); void MakeEmpty (Queue Q);
void Enqueue (int X, Queue Q); void Dequeue (Queue Q); struct node
{
int data ; position next;
}* Front = NULL, *Rear = NULL;
- Queue Empty Operation:
- Initially Queue is Empty.
- With Linked List implementation, Empty Queue is represented as S -> next = NULL.
- It is necessary to check for Empty Queue before deleting the front element in the Queue.
ROUTINE TO CHECK WHETHER THE QUEUE IS EMPTY
int IsEmpty (Queue Q
{
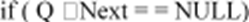
return (1)
}
- EnQueue Operation Empty Queue
- It is the process of inserting a new element at the Rear end of the Queue.
- It takes two parameters, EnQueue ( int X , Queue Q ). The elements X to be inserted into the Queue Q.
- Using malloc ( ) function allocate memory for the newnode to be inserted into the Queue.
- If the Queue is Empty, the newnode to be inserted will become first and last node in the list. Hence Front and Rear points to the newnode.
- Otherwise insert the newnode in the Rear -> next and update the Rear pointer.
Routine to EnQueue an Element in Queue
void EnQueue ( int X, Queue Q )
{
struct node *newnode;
newnode = malloc (sizeof (struct node)); if (Rear = = NULL)
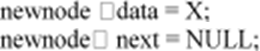
{
Q -> next = newnode; Front = newnode; Rear = newnode;
}
else

{
Rear = newnode;
}
}
- DeQueue Operation
It is the process of deleting the front element from the Queue.
After Insertion
It takes one parameter, Dequeue ( Queue Q ). Always element in the front (i.e) element pointed by Q -> next is deleted always.
Element to be deleted is made “temp”.
If the Queue is Empty, then deletion is not possible.
If the Queue has only one element, then the element is deleted and Front and Rear pointer is made NULL to represent Empty Queue.
Otherwise, Front element is deleted and the Front pointer is made to point to next node in the list. The free ( ) function informs the compiler that the address that temp is pointing to, is unchanged but the data present in that address is now undefined.
Routine to DeQueue an Element from the Queue
void DeQueue ( Queue Q )
{
struct node *temp;
if ( Front = = NULL )
Error (“Empty Queue!!! Deletion not possible.” ); else if (Front = = Rear)
{
temp = Front;
Q -> next = NULL; Front = NULL; Rear = NULL;
free ( temp );
}
else
{
temp = Front;
Q -> next = temp -> next; Front = Front àNext; free (temp);
}
}
Linked list implementation of Queue
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void enqueue(); void dequeue(); void display();
typedef struct node *position;
position front=NULL,rear=NULL,newnode,temp,p;
struct node
{
int data; position next;
};
void main()
{
int choice; clrscr(); do
{
printf(“1.Enqueue\n2.Dequeue\n3.display\n4.exit\n”); printf(“Enter your choice\n\n”);
scanf(“%d”,&choice); switch(choice)
{
case 1:
enqueue(); break;
case 2:
dequeue(); break;
case 3:
display(); break;
case 4:
exit(0);
}
}
while(choice<5);
}
void enqueue()
{
newnode=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); printf(“\n Enter the data to be enqueued\n”); scanf(“%d”,&newnode->data);
newnode->next=NULL; if(rear==NULL)
front=rear=newnode; else {
rear->next=newnode; rear=newnode;
}
display();
}
void dequeue()
{
if(front==NULL)
printf(“\nEmpty queue!!!!! Deletion not possible\n”); else if(front==rear)
{
printf(“\nFront element %d is deleted from queue!!!! now queue is empty!!!! no more deletion possible!!!!\n”,front->data);
front=rear=NULL;
}
else
{
temp=front; front=front->next;
printf(“\nFront element %d is deleted from queue!!!!\n”,temp->data); free(temp);
}
display();
}
void display()
{
p=front; while(p!=NULL)
{
printf(“%d -> “,p->data); p=p->next;
}
printf(“Null\n”);
}
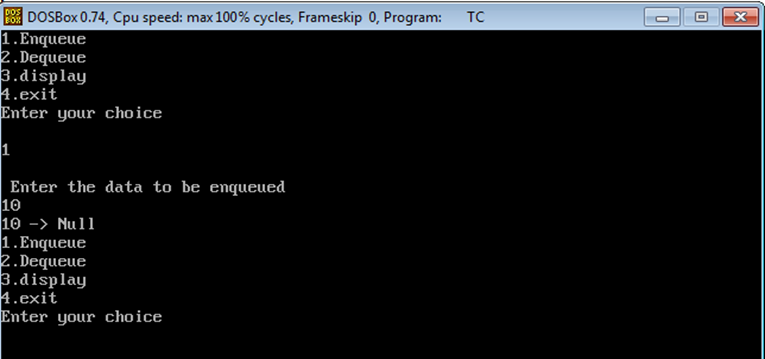
Output
Other courses
