- A circular queue is an abstract data type that contains a collection of data which allows addition of data at the end of the queue and removal of data at the beginning of the queue.
- Circular queues have a fixed size.Circular queue follows FIFO principle.
- Queue items are added at the rear end and the items are deleted at front end of the circular queue
Here the Queue space is utilized
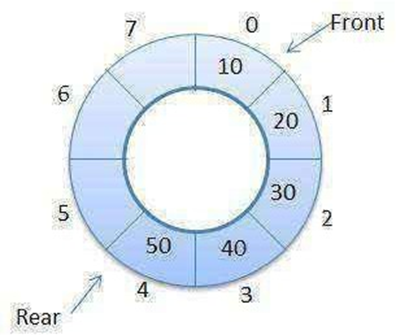
Operations on Circular Queue
Fundamental operations performed on the Circular Queue are
- Circular Queue Enqueue
- Circular Queue Dequeue
Formula to be used in Circular Queue
For Enqueue Rear = ( Rear + 1) % ArraySize For Dequeue Front = ( Front + 1) % ArraySize
(i) Circular Queue Enqueue Operation
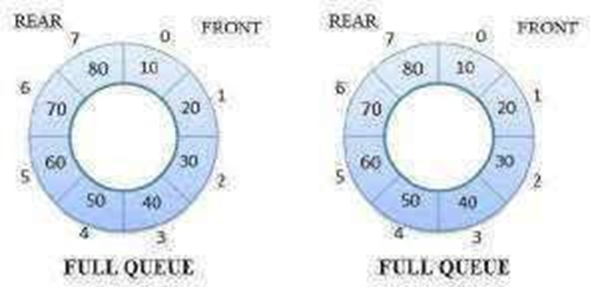
It is same as Linear Queue EnQueue Operation (i.e) Inserting the element at the Rear end. First check for full Queue.
If the circular queue is full, then insertion is not possible. Otherwise check for the rear end.
If the Rear end is full, the elements start getting inserted from the Front end.
Routine to Enqueue an element in circular queue
void Enqueue ( int X, CircularQueue CQ )
{
if( Front = = ( Rear + 1 ) % ArraySize)
Error( “Queue is full!!Insertion not possible” ); else if( Rear = = -1 )
{
Front = Front + 1; Rear = Rear + 1; CQ[ Rear ] = X;
}
else
{
Rear = ( Rear + 1 ) % Arraysize; CQ[ Rear ] = X;
}
}
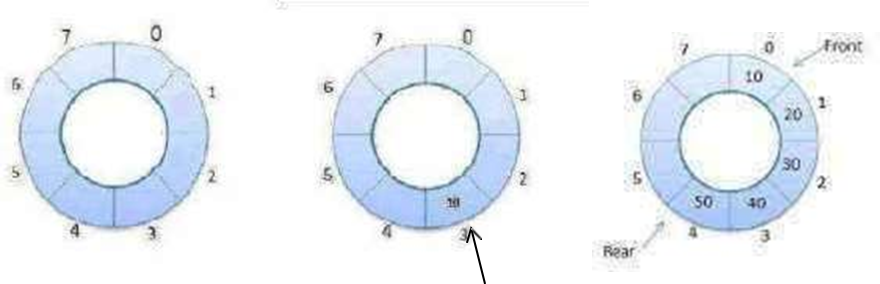
Routine To DeQueue An Element In Circular Queue
void DeQueue (CircularQueue CQ)
{
if(Front== – 1) Empty(“Empty Queue!”);
else if(Front==rear)
{
X=CQ[Front]; Front=-1; Rear=-1;
}
else
{
X=CQ[Front]; Front=(Front+1)%Arraysize;
}}
Implementation of Circular Queue
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #define max 3
void insert(); void delet(); void display(); int q[10],front=0,rear=-1;
void main()
{ int ch; clrscr();
printf(“\nCircular Queue operations\n”); printf(“1.insert\n2.delete\n3.display\n4.exit\n”); while(1)
{
printf(“Enter your choice:”); scanf(“%d”,&ch); switch(ch)
{
case 1:
insert(); break; case 2:
delet(); break; case 3:
display(); break;
case 4:
exit();
default:
printf(“Invalid option\n”);
}}}
void insert()
{
int x;
if((front==0&&rear==max-1)||(front>0&&rear==front-1)) printf(“Queue is overflow\n”);
else
{
printf(“Enter element to be insert:”); scanf(“%d”,&x);
if(rear==max-1&&front>0)
{ rear=0; q[rear]=x;
}
else
{
if((front==0&&rear==-1)||(rear!=front-1)) q[++rear]=x;
} }}
void delet()
{
int a; if((front==0)&&(rear==-1))
printf(“Queue is underflow\n”); if(front==rear)
{
a=q[front]; rear=-1; front=0;
}
else if(front==max-1)
{
a=q[front]; front=0;
}
else
a=q[front++];
printf(“Deleted element is:%d\n”,a);
}
void display()
{
int i,j; if(front==0&&rear==-1) printf(“Queue is underflow\n”); if(front>rear) { for(i=0;i<=rear;i++) printf(“\t%d”,q[i]); for(j=front;j<=max-1;j++) printf(“\t%d”,q[j]);
printf(“\nrear is at %d\n”,q[rear]); printf(“\nfront is at %d\n”,q[front]); } else
{
for(i=front;i<=rear;i++) printf(“\t%d”,q[i]); printf(“\nrear
is at %d\n”,q[rear]); printf(“\nfront is at %d\n”,q[front]);
}
printf(“\n”);
}
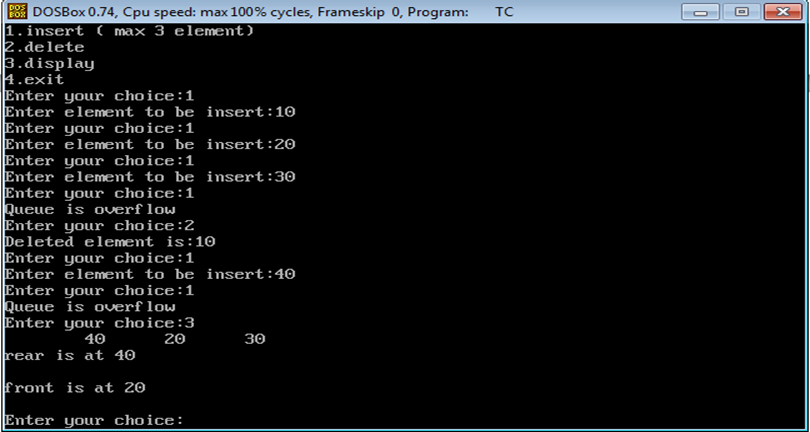
OUTPUT
Other courses
