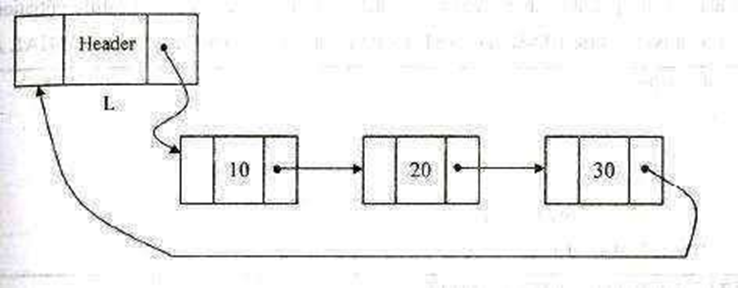
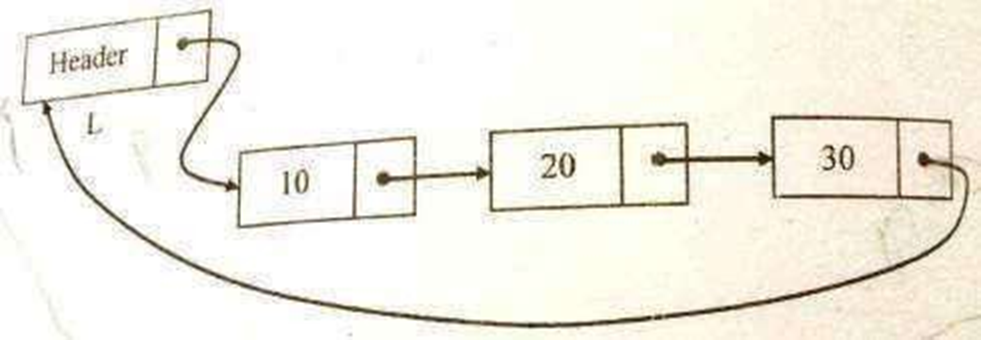
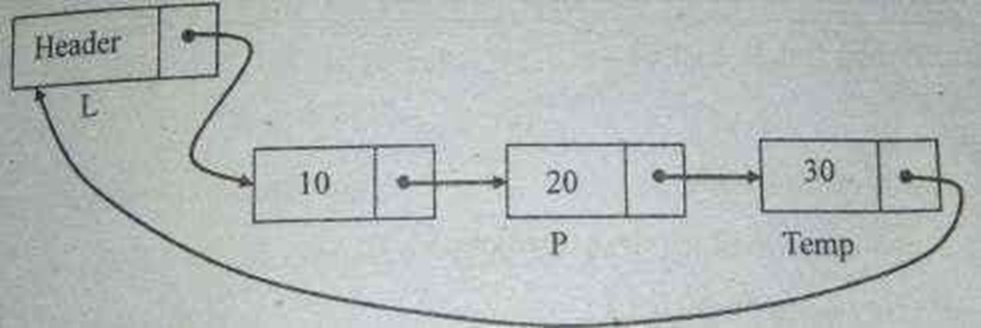
Circular Linked list is a linked list in which the pointer of the last node points to the first node
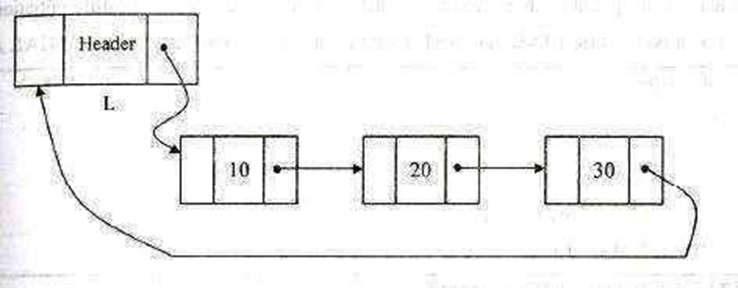
Types of CLL:
CLL can be implemented as circular singly linked list and circular doubly linked list.
Singly linked circular list:
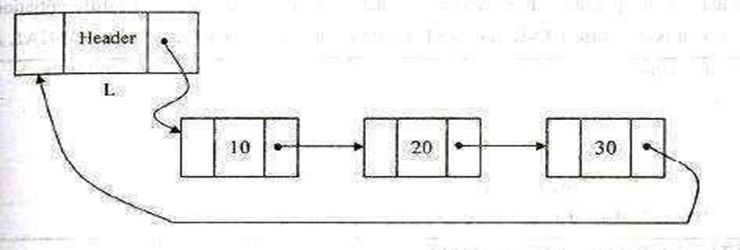
A Singly linked circular list is a linked list in which the last node of the list points to the first node.
Declaration of node:
typedef struct node *position; struct node
{
int data; position next;
};
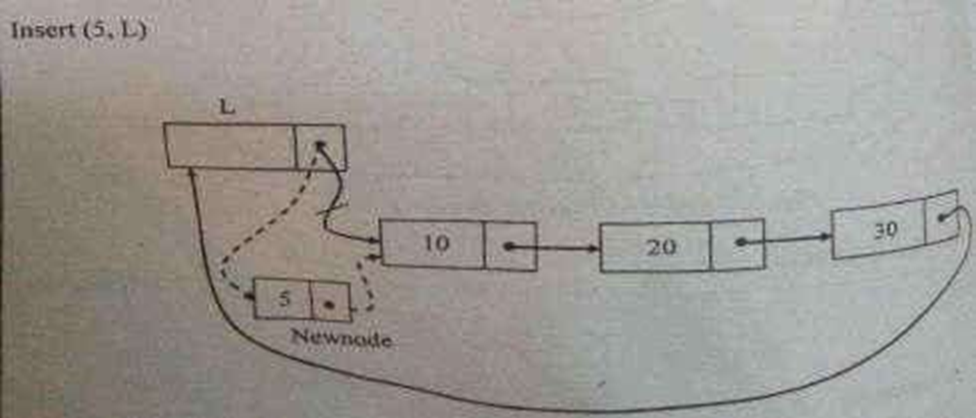
Routine to insert an element in the beginning
void insert_beg(int X,List L)
{
position Newnode;
Newnode=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); if(Newnode!=NULL)
{
Newnode->data=X;
Newnode->next=L->next;
L->next=Newnode;
}
}
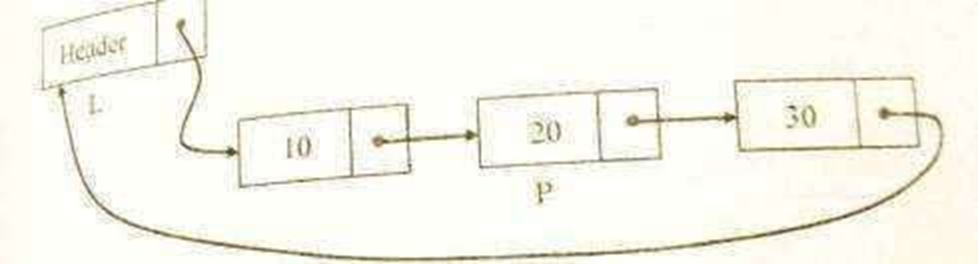
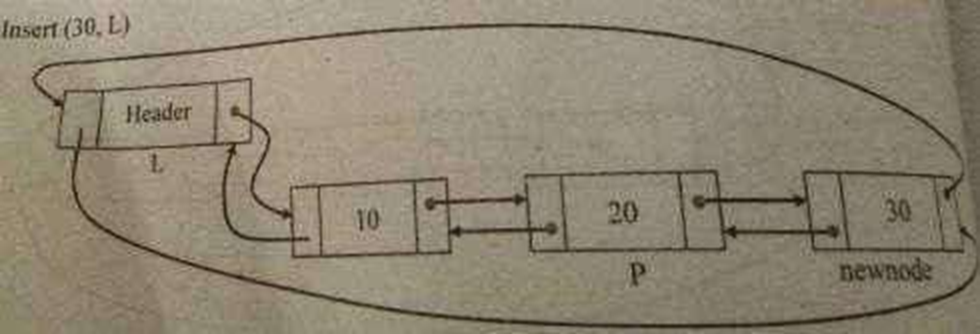
Routine to insert an element in the middle
void insert_mid(int X, List L, Position p)
{
position Newnode;
Newnode=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); if(Newnode!=NULL)
{
Newnode->data=X; Newnode->next=p->next; p->next=Newnode;
}
}
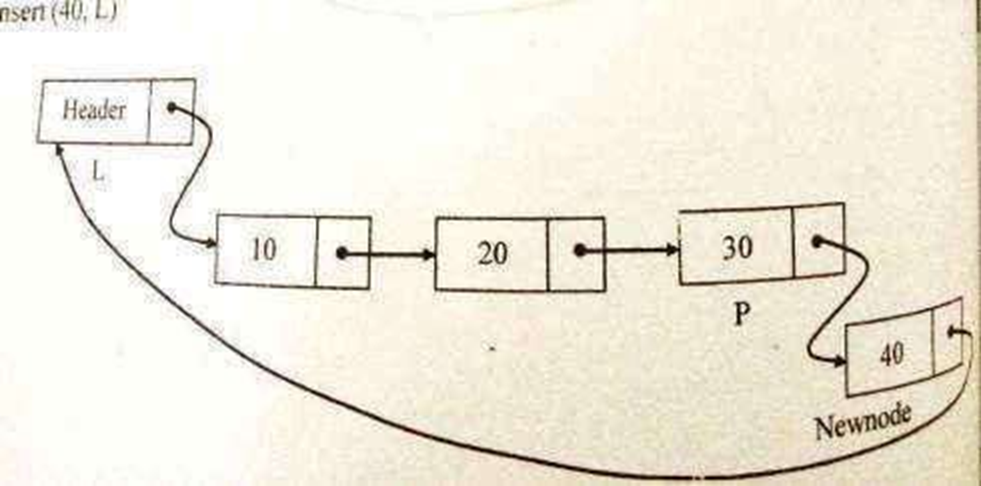
Routine to insert an element in the last
void insert_last(int X, List L) position Newnode;
Newnode=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); if(Newnode!=NULL)
{ P=L;
while(P->next!=L) P=P->next; Newnode->data=X; P->next=Newnode; Newnode->next=L;
}
}
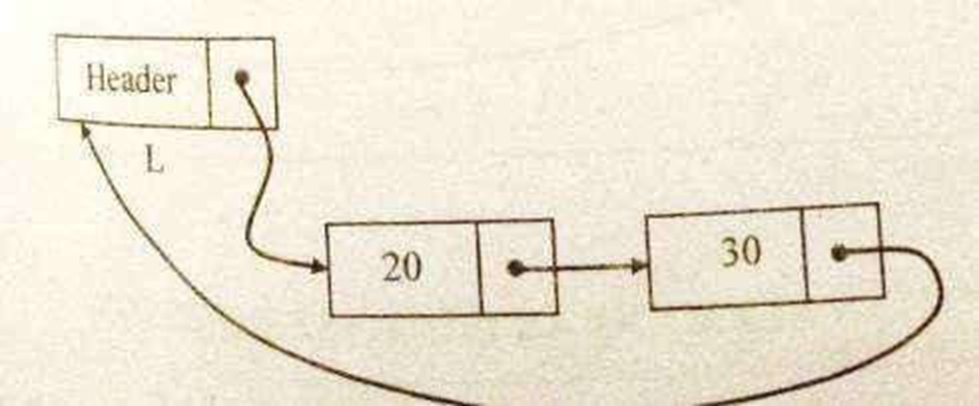
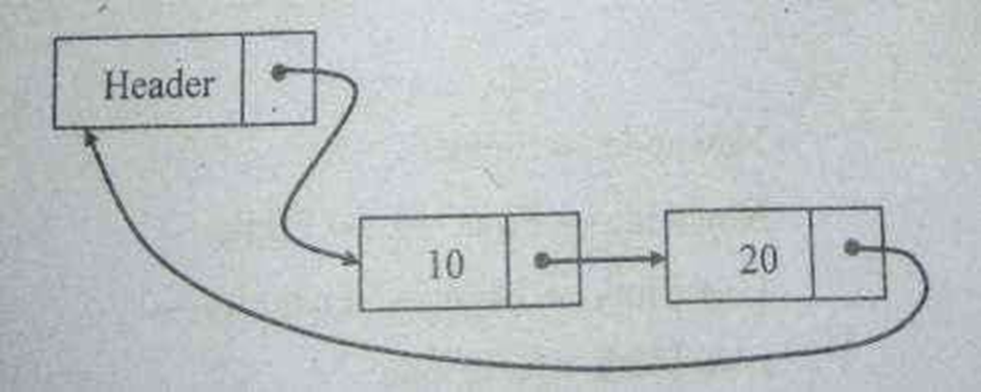
Routine to delete an element from the beginning
void del_first(List L)
{
position temp; temp=L->next;
L->next=temp->next; free(temp);
}
www.padeepz.net
Routine to delete an element from the middle
void del_mid(int X,List L)
{
position p, temp; p=findprevious(X,L); if(!Islast(P,L))
{
temp=p->next;
p->next=temp->next; free(temp);
}
}
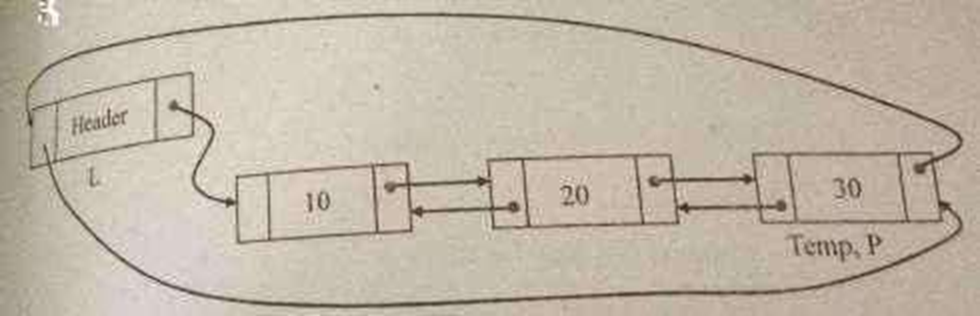
Routine to delete an element at the last position
void del_last(List L)
{
position p, temp; p=L;
while(p->next->next!=L) p=p->next;
temp=p->next; p->next=L free(temp);}
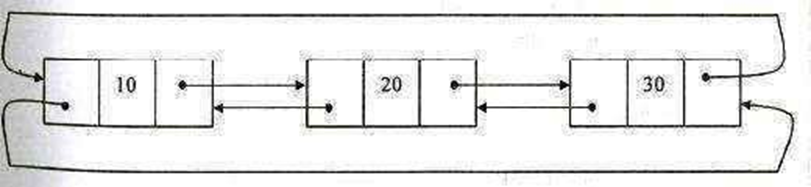
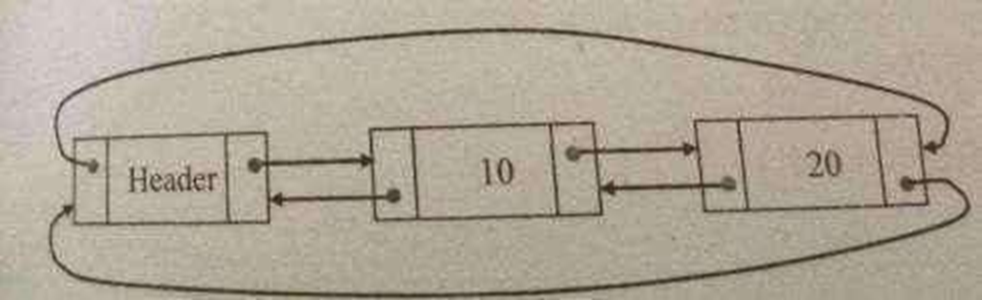
Doubly Linked circular list:
A doubly linked circular list is a doubly linked list in which the next link of the last node points to the first node and prev link of the first node points to the last node of the list.
Declaration of node:
typedef struct node *position; struct node
{
int data; position next; position prev;
};
Routine to insert an element in the beginning
void insert_beg(int X,List L)
{
position Newnode;
Newnode=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); if(Newnode!=NULL)
{
Newnode->data=X;
Newnode->next=L->next;
L->next->prev=Newnode;
L->next=Newnode;
Newnode->prev=L;
}
}
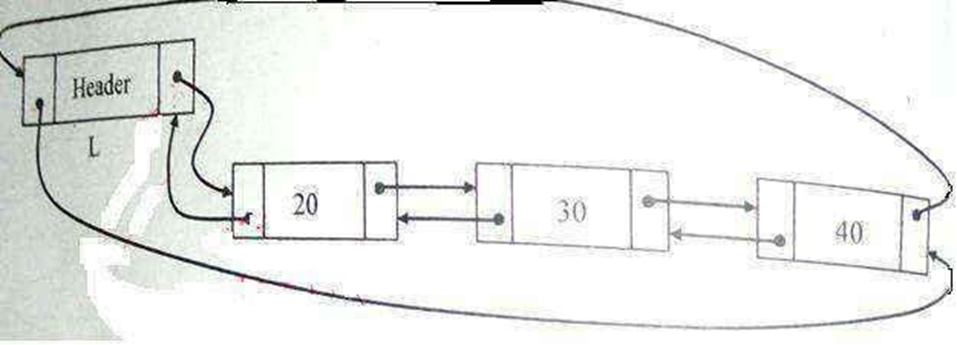
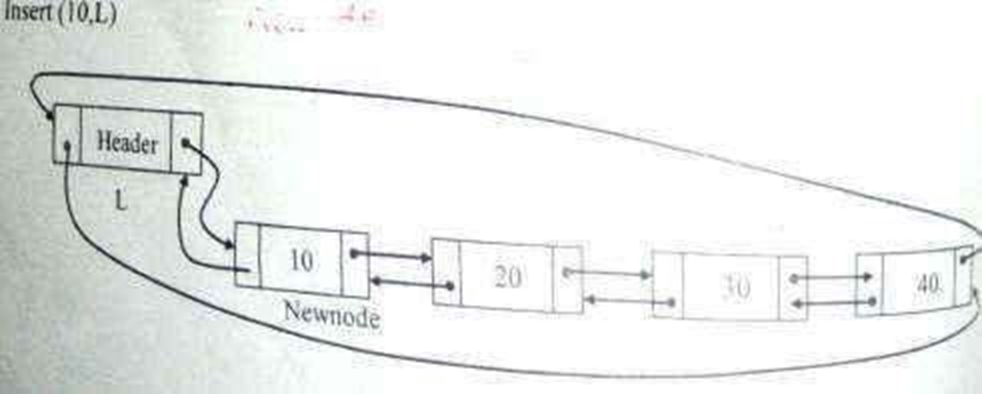
Routine to insert an element in the last
void insert_last(int X, List L)
{
position Newnode,p;
Newnode=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); if(Newnode!=NULL)
{ p=L;
while(p->next!=L) p=p->next; Newnode->data=X; p->next =Newnode; Newnode->next=L; Newnode->prev=p; L->prev=newnode;
}
}
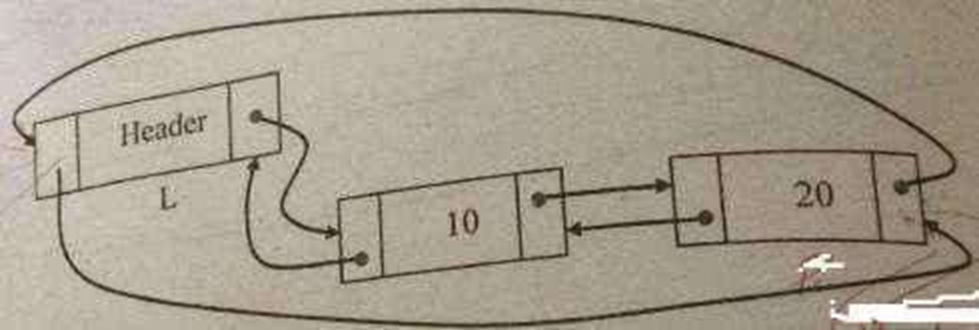
Routine to delete an element from the beginning
void del_first(List L)
{
position temp;
if(L->next!=NULL)
{
temp=L->next;
L->next=temp->next; temp->next->prev=L; free(temp);
}
Advantages of Circular linked List
It allows to traverse the list starting at any point.
It allows quick access to the first and last records.
Circularly doubly linked list allows to traverse the list in either direction.
Applications of List:
- Polynomial ADT
- Radix sort
- 3.Multilist
Other courses
