A doubly linked list is a linked list in which each node has three fields namely Data, Next, Prev. Data-This field stores the value of the element
Next-This field points to the successor node in the list
Prev-This field points to the predecessor node in the list
| PREV | DATA | NEXT |
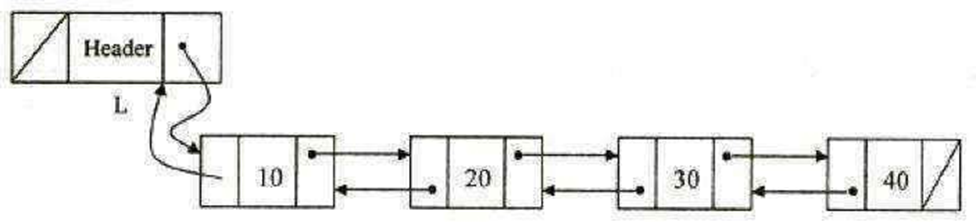
Basic operations of a doubly -linked list are:
- Insert – Inserts a new element at the end of the list.
- Delete – Deletes any node from the list.
- Find – Finds any node in the list.
- Print – Prints the list
Declaration of DLL Node
Basic operations of a doubly -linked list are:
- Insert – Inserts a new element at the end of the list.
- Delete – Deletes any node from the list.
- Find – Finds any node in the list.
- Print – Prints the list
Declaration of DLL Node
| PREV DATA NEXT |
DATA
NEXT
typedef struct node *position ; struct node
{
int data;
position prev; position next;
};
Creation of list in DLL
Initially the list is empty. Then assign the first node as head. newnode->data=X;
newnode->next=NULL;
list.
newnode->prev=NULL; L=newnode;
If we add one more node in the list,then create a newnode and attach that node to the end of the
L->next=newnode; newnode->prev=L;
Routine to insert an element in a DLL at the beginning
void Insert (int x, list L, position P){ struct node *Newnode;
if(pos==1) P=L;
Newnode = (struc node*)malloc (sizeof(struct node)); if (Newnode! = NULL)
Newnode->data= X; Newnode ->next= L ->next; L->next ->prev=Newnode L->next = Newnode; Newnode ->prev = L;
}
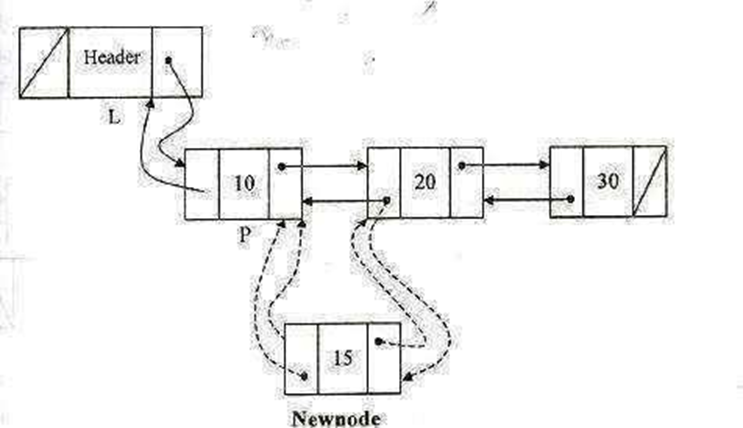
Routine to insert an element in a DLL any position :
void Insert (int x, list L, position P)
{
struct node *Newnode;
Newnode = (struc node*)malloc (sizeof(struct node)); if (Newnode! = NULL)
Newnode->data= X; Newnode ->next= P ->next; P->next ->prev=Newnode P ->next = Newnode; Newnode ->prev = P:
}
Routine to insert an element in a DLL at the end:
void insert(int X, List L, position p)
{
p=L;
newnode=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
printf(“\nEnter the data to be inserted\n”); scanf(“%d”,&newnode->data);
while(p->next!=NULL) p=p->next;
newnode->next=NULL; p->next=newnode; newnode->prev=p;
}
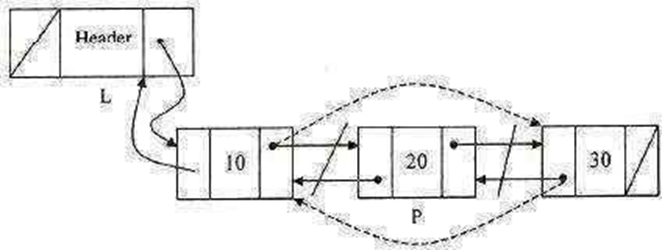
Routine for deleting an element:
void Delete (int x ,List L)
{
Position p , temp; P = Find( x, L ); if(P==L->next) temp=L;
L->next=temp->next; temp->next->prev=L; free(temp);
elseif( IsLast( p, L ) )
{
temp = p;
p -> prev -> next = NULL; free(temp);
}
else
{
temp = p;
p -> prev -> next = p -> next; p -> next -> prev = p -> prev; free(temp);
}
Routine to display the elements in the list:
void Display( List L )
{
P = L -> next ; while ( p != NULL)
{
printf(“%d”, p -> data ; p = p -> next ;
}
printf(“ NULL”);
}
Routine to search whether an element is present in the list
void find()
{
int a,flag=0,count=0; if(L==NULL)
printf(“\nThe list is empty”); else
{
printf(“\nEnter the elements to be searched”); scanf(“%d”,&a);
for(P=L;P!=NULL;P=P->next)
{
count++;
if(P->data==a)
{
flag=1;
printf(“\nThe element is found”); printf(“\nThe position is %d”,count);
break;
}
}
if(flag==0)
printf(“\nThe element is not found”);
}
}
| Program Implementation of Doubly linked list | Output |
| #include<conio.h> void insert(); void deletion(); void display(); void find(); typedef struct node *position; position newnode,temp,L=NULL,P; struct node { int data; position next; position prev; }; void main() { int choice; clrscr(); do { printf(“\n1.INSERT”); printf(“\n2.DELETE”); printf(“\n3.DISPLAY”); printf(“\n4.FIND”); printf(“\n5.EXIT”); printf(“\nEnter ur option”); scanf(“%d”,&choice); switch(choice) { case 1: insert(); break; case 2: deletion(); break; case 3: display(); | INSERT DELETE DISPLAY FIND EXIT Enter your option1 Enter the data be inserted10 INSERT DELETE DISPLAY FIND EXIT Enter your option1 Enter the data to be inserted 20 Enter the position where |
| the data is to be inserted 2 |
| break; case 4: find(); break; case 5: exit(1); } }while(choice!=5); getch(); } void insert() { int pos,I; newnode=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); printf(“\nEnter the data to be inserted”); scanf(“%d”,&newnode->data); if(L==NULL) { L=newnode; L->next=NULL; L->prev=NULL; } else { printf(“\nEnter the position where the data is to be inserted”); scanf(“%d”,&pos); if(pos==1) { newnode->next=L; newnode->prev=NULL; L->prev=newnode; L=newnode; } else { P=L; for(i=1;i<pos-1&&P->next!=NULL;i++) { P=P->next; } newnode->next=P->next; P->next=newnode; newnode->prev=P; P->next->prev=newnode; } | INSERT DELETE DISPLAY FIND EXIT Enter your option1 Enter the data to be inserted 30 Enter the position where the data is to be inserted3 INSERT DELETE DISPLAY FIND EXIT Enter your option 3 The elements in the list are 10 20 30 INSERT DELETE DISPLAY FIND EXIT Enter your option 2 |
| } void deletion() { int pos,I; if(L==NULL) printf(“\nThe list is empty”); else { printf(“\nEnter the position of the data to be deleted”); scanf(“%d”,&pos); if(pos==1) { temp=L; L=temp->next; L->prev=NULL; printf(“\nThe deleted element is %d”,temp->data); free(temp); } else { P=L; for(i=1;i<pos-1;i++) P=P->next; temp=P->next; printf(“\nThe deleted element is %d”,temp->data); P->next=temp->next; temp->next->prev=P; free(temp); } } } void display() { if(L==NULL) printf(“\nNo of elements in the list”); else { printf(“\nThe elements in the listare\n”); for(P=L;P!=NULL;P=P->next) printf(“%d”,P->data); } } void find() { int a,flag=0,count=0; | Enter the position of the data to be deleted 2 The deleted element is 20 INSERT DELETE DISPLAY FINDEXIT Enter your option 3 The elements in the list are 10 30 INSERT DELETE DISPLAY FIND EXIT Enter your option4 Enter the elements to be searched 20 The element is not found INSERT DELETE DISPLAY FIND EXIT Enter your option 4 |
| if(L==NULL) printf(“\nThe list is empty”); else { printf(“\nEnter the elements to be searched”); scanf(“%d”,&a); for(P=L;P!=NULL;P=P->next) { count++; if(P->data==a) { flag=1; printf(“\nThe element is found”); printf(“\nThe position is %d”,count); break; } } if(flag==0) printf(“\nThe element is not found”); } | Enter the elements to be searched 30 The element is found The position is 2 INSERT DELETE DISPLAY FIND EXIT Enter your option5 Press any key to continue . . . |
Advantages of DLL:
The DLL has two pointer fields. One field is prev link field and another is next link field. Because of these two pointer fields we can access any node efficiently whereas in SLL only one link field is there which stores next node which makes accessing of any node difficult.
Disadvantages of DLL:
The DLL has two pointer fields. One field is prev link field and another is next link field. Because of these two pointer fields, more memory space is used by DLL compared to SLL
Other Courses
Power BI
