Data: A collection of facts, concepts, figures, observations, occurrences or instructions in a
formalized manner.
Information:The meaning that is currently assigned to data by means of the conventions applied to those data(i.e. processed data)
Record:Collection of related fields.
Data type:Set of elements that share common set of properties used to solve a program.
Data Structures:
Data Structure is the way of organizing, storing, and retrieving data and their relationship with each other.
Characteristics of data structures:
- It depicts the logical representation of data in computer memory.
- It represents the logical relationship between the various data elements.
- It helps in efficient manipulation of stored data elements.
- It allows the programs to process the data in an efficient manner.
Operations on Data Structures:
- Traversal
- Search
- Insertion
- Deletion
CLASSIFICATION OF DATA STRUCTURES
Primary Data Strucutre/Primitive Data Structures:
Primitive data structures include all the fundamental data structures that can be directly
manipulated by machine-level instructions. Some of the common primitive data structures include integer, character, real, boolean etc
Secondary Data Structures/Non Primitive Data Structures:
Non primitive data structures, refer to all those data structures that are derived from one or more primitive data structures. The objective of creating non-primitive data structures is to form sets of homogeneous or heterogeneous data elements.
Linear Data Structures:
Linear data structures are data strucutres in which, all the data elements are arranged in i, linear or sequential fashion. Examples of data structures include arrays, stacks, queues, linked lists, etc.
Non Linear Structures:
In non-linear data strucutres, there is definite order or sequence in which data elements are arranged.
For instance, a non-linear data structures could arrange data elements in a hierarchical fashion. Examples of non-linear data structures are trees and graphs.
Static and dynamic data structure:
Static Ds:
If a ds is created using static memory allocation, ie. ds formed when the number of data items are known in advance ,it is known as static data static ds or fixed size ds.
Dynamic Ds:
If the ds is created using dynamic memory allocation i.e ds formed when the number of data items are not known in advance is known as dynamic ds or variable size ds.
Application of data structures:
Data structures are widely applied in the following areas:
Compiler design
Operating system
Statistical analysis package
DBMS
Numerical analysis
Simulation
Artificial intelligence
Graphics
Abstract Data type:
An abstract Data type (ADT) is defined as a mathematical model with a collection of operations defined on that model. Set of integers, together with the operations of union, intersection and set difference form a example of an ADT. An ADT consists of data together with functions that operate on that data.
Advantages/Benefits of ADT:
- Modularity 2.Reuse
- code is easier to understand
- Implementation of ADTs can be changed without requiring changes to the program that uses the ADTs.
THE LIST AI)T:
List is an ordered set of elements.
The general form of the list is A1 ,A2 , ……,AN A1 – First element of the list
A2- 1st element of the list
N –Size of the list
If the element at position i is Ai, then its successor is Ai+1 and its predecessor is Ai-1
Various operations performed on List
- Insert (X, 5)- Insert the element X after the position 5.
- Delete (X) – The element X is deleted
- Find (X) – Returns the position of X.
- Next (i) – Returns the position of its successor element i+1.
- Previous (i) Returns the position of its predecessor i-1.
- Print list – Contents of the list is displayed.
- Makeempty- Makes the list empty.
Implementation of list ADT:
- Array based Implementation
- Linked List based implementation
Array Implementation of list:
It is a collection of specific number of same type of data stored in consecutive memory locations. Array is a static data structure i.e., the memory should be allocated in advance and the size is fixed. This will waste the memory space when used space is less than the allocated space.
Insertion and Deletion operation are expensive as it requires more data movements Find and Print list operations takes constant time.
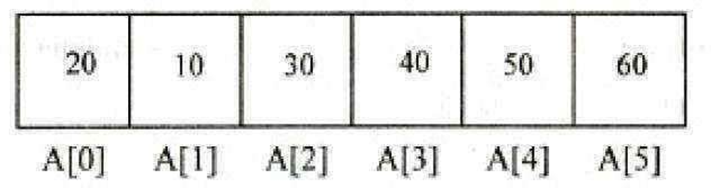
The basic operations performed on a list of elements are
- Creation of List.
- Insertion of data in the List
- Deletion of data from the List
- Display all data‟s in the List
- Searching for a data in the list
Declaration of Array:
#define maxsize 10 int list[maxsize], n ;
Create Operation:
Create operation is used to create the list with „ n „ number of elements .If „ n „ exceeds the array‟s maxsize, then elements cannot be inserted into the list. Otherwise the array elements are stored in the consecutive array locations (i.e.) list [0], list [1] and so on.
void Create ( )
{
int i;
printf(“\nEnter the number of elements to be added in the list:\t”); scanf(“%d”,&n);
printf(“\nEnter the array elements:\t”); for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf(“%d”,&list[i]);
}
If n=6, the output of creation is as follows:
list[6]
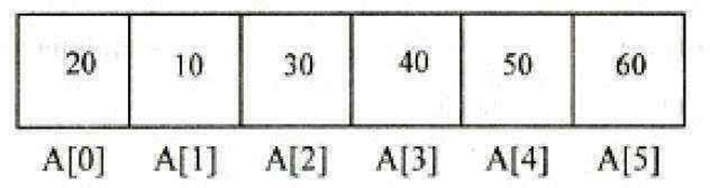
Insert Operation:
Insert operation is used to insert an element at particular position in the existing list. Inserting the element in the last position of an array is easy. But inserting the element at a particular position in an array is quite difficult since it involves all the subsequent elements to be shifted one position to the right.
Routine to insert an element in the array:
void Insert( )
{
int i, data, pos;
print f(“\n Enter the data to be inserted:\t”); scan f(“%d”,& data);
print f(“\n Enter the position at which element to be inserted:\t”); scan f(“%d”,& pos);
if (pos==n)
print f (“Array overflow”); for(i = n-1 ; i >= pos-1 ; i–)
list[i+1] = list[i]; list[pos-1] = data; n=n+1;
Display();}
Deletion Operation:
Deletion is the process of removing an element from the array at any position.
Deleting an element from the end is easy. If an element is to be deleted from any particular position ,it requires all subsequent element from that position is shifted one position towards left.
Routine to delete an element in the array:
void Delete( )
{
int i, pos ;
print f(“\nEnter the position of the data to be deleted:\t”); scanf(“%d”,&pos);
print f(“\nThe data deleted is:\t %d”, list[pos-1]); for(i=pos-1;i<n-1;i++)
list[i]=list[i+1]; n=n-1;
Display();
}
Display Operation/Traversing a list
Traversal is the process of visiting the elements in a array.
Display( ) operation is used to display all the elements stored in the list. The elements are stored from the index 0 to n – 1. Using a for loop, the elements in the list are viewed
Routine to traverse/display elements of the array:
void display( )
{
int i;
printf(“\n**********Elements in the array**********\n”); for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf(“%d\t”,list[i]);
}
Search Operation:
Search( ) operation is used to determine whether a particular element is present in the list or not. Input the search element to be checked in the list.
Routine to search an element in the array:
void Search( )
{
int search,i,count = 0;
printf(“\nEnter the element to be searched:\t”); scanf(“%d”,&search);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(search == list[i]) count++;
}
if(count==0)
printf(“\nElement not present in the list”); else
printf(“\nElement present in the list”);
}
Program for array implementation of List
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #define maxsize 10 int list[maxsize],n; void Create();
void Insert(); void Delete(); void Display(); void Search(); void main()
{ int choice; clrscr(); do
{
printf(“\n Array Implementation of List\n”); printf(“\t1.create\n”);
printf(“\t2.Insert\n”); printf(“\t3.Delete\n”); printf(“\t4.Display\n”); printf(“\t5.Search\n”); printf(“\t6.Exit\n”); printf(“\nEnter your choice:\t”); scanf(“%d”,&choice); switch(choice)
{
case 1: Create();
break; case 2: Insert();
break; case 3: Delete();
break; case 4: Display();
break; case 5: Search();
break; case 6: exit(1);
default: printf(“\nEnter option between 1 – 6\n”); break;
}
}while(choice<7);
}
void Create()
{
int i;
printf(“\nEnter the number of elements to be added in the list:\t”); scanf(“%d”,&n);
printf(“\nEnter the array elements:\t”); for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf(“%d”,&list[i]); Display();
}
void Insert()
{
int i,data,pos;
printf(“\nEnter the data to be inserted:\t”); scanf(“%d”,&data);
printf(“\nEnter the position at which element to be inserted:\t”); scanf(“%d”,&pos);
for(i = n-1 ; i >= pos-1 ; i–) list[i+1] = list[i];
list[pos-1] = data; n+=1;
Display();
}
void Delete( )
{
int i,pos;
printf(“\nEnter the position of the data to be deleted:\t”); scanf(“%d”,&pos);
printf(“\nThe data deleted is:\t %d”, list[pos-1]); for(i=pos-1;i<n-1;i++)
list[i]=list[i+1]; n=n-1; Display();
}
void Display()
{
int i;
printf(“\n**********Elements in the array**********\n”); for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf(“%d\t”,list[i]);
}
void Search()
{
int search,i,count = 0;
printf(“\nEnter the element to be searched:\t”); scanf(“%d”,&search);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(search == list[i])
{
count++;
}
}
if(count==0)
printf(“\nElement not present in the list”); else
printf(“\nElement present in the list”);
}
Output
Array Implementation of List 1.create
- Insert 3.Delete 4.Display 5.Search 6.Exit
Enter your choice: 1
Enter the number of elements to be added in the list: 5 Enter the array elements: 1 2 3 4 5
**********Elements in the array**********
1 2 3 4 5
Array Implementation of List 1.create
2.Insert 3.Delete 4.Display 5.Search 6.Exit
Enter your choice: 2
Enter the data to be inserted: 3
Enter the position at which element to be inserted: 1
**********Elements in the array**********
3 1 2 3 4 5
Array Implementation of List 1.create
2.Insert 3.Delete 4.Display 5.Search 6.Exit
Enter your choice: 3
Enter the position of the data to be deleted: 4 The data deleted is: 3
**********Elements in the array**********
3 1 2 4 5
Array Implementation of List 1.create
2.Insert 3.Delete 4.Display 5.Search 6.Exit
Enter your choice: 5
Enter the element to be searched: 1 Element present in the list
Array Implementation of List
- create
- Insert 3.Delete 4.Display 5.Search 6.Exit
Enter your choice:6
OTHER COURSES
