. Power BI Desktop is designed to empower business analysts, data professionals, and decision-makers to create insightful and impactful data visualizations. It’s a powerful tool for transforming raw data into meaningful insights and communicating those insights effectively.
In Power BI, data storage can occur in several locations depending on the connectivity mode and specific configurations. Here are the primary locations where data can be stored in Power BI:
1. Power BI Service (Cloud):
– When using the Import mode, data is imported into and stored within the Power BI service. The data is loaded into memory and stored in a compressed format in the Power BI dataset in the cloud.
– Power BI service also stores metadata, reports, and dashboards, enabling sharing and collaboration across users.
2. On-premises Data Sources:
– For Direct Query mode, data remains in the original on-premises data source. Queries are executed live against these sources, and no data is imported into Power BI.
– Live Connection mode, typically used with SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) or Azure Analysis Services, also keeps data in the original data source, with Power BI serving as a visualization layer.
3. Power BI Desktop (Local):
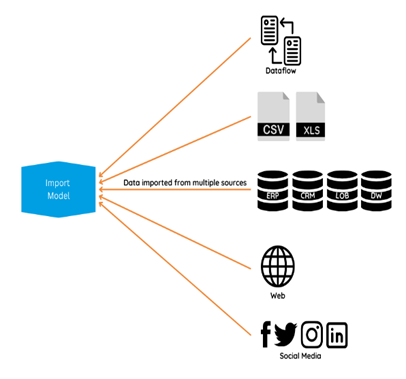
– When working with Power BI Desktop, data imported from various sources is stored within the Power BI Desktop file . This file includes the data model, transformations, visualizations, and other report elements.
– Data in the .pbix file is stored locally on the user’s machine until the report is published to the Power BI service.
4. Dataflows:
– Power BI Dataflows enable ETL processes and data storage in the Power BI service using Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS). Data is stored in a structured and reusable manner within the cloud.
– Dataflows can be used to centralize and manage data transformations and storage across multiple Power BI reports.
5. Azure Services:
– Power BI can integrate with various Azure services, such as Azure SQL Database, Azure Synapse Analytics, and Azure Blob Storage. When connected via Direct Query or Live Connection, data remains in these Azure services.
– Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) is often used in conjunction with Power BI Dataflows for scalable and efficient data storage.
The choice of data storage location depends on factors like data size, refresh frequency, performance requirements, and organizational data governance policies.
In Power BI, data can be stored in several ways depending on the type of dataset and the connection mode being used. Here are the primary storage options:
- Import Mode:
- Power BI Service: When you import data into Power BI, the data is stored within the Power BI Service. This data is kept in the dataset associated with your report or dashboard, and it is loaded into memory for quick access and query performance.
- Power BI Desktop: When working in Power BI Desktop, the imported data is stored within the .pbix file. This file contains both the data and the report definition.
- Direct Query Mode:
- Source System: In Direct Query mode, the data is not stored within Power BI. Instead, queries are sent directly to the underlying data source, such as a SQL Server, Oracle database, or other supported databases. The data remains in the source system and is queried in real-time whenever a user interacts with the report.
- Live Connection Mode:
- Source System: Similar to Direct Query, in Live Connection mode, the data stays in the original data source (such as SQL Server Analysis Services or Power BI datasets). The reports query the live data source directly without storing the data in Power BI.
- Composite Models:
- Combination: Composite models allow you to use a combination of Import and Direct Query modes. Some data can be imported and stored within Power BI, while other data can be queried live from the source system.
In summary, Power BI stores data either within the Power BI Service (for imported data) or in the original data source (for Direct Query and Live Connection modes). The choice of storage depends on the connection mode and the specific requirements of the report or dashboard.