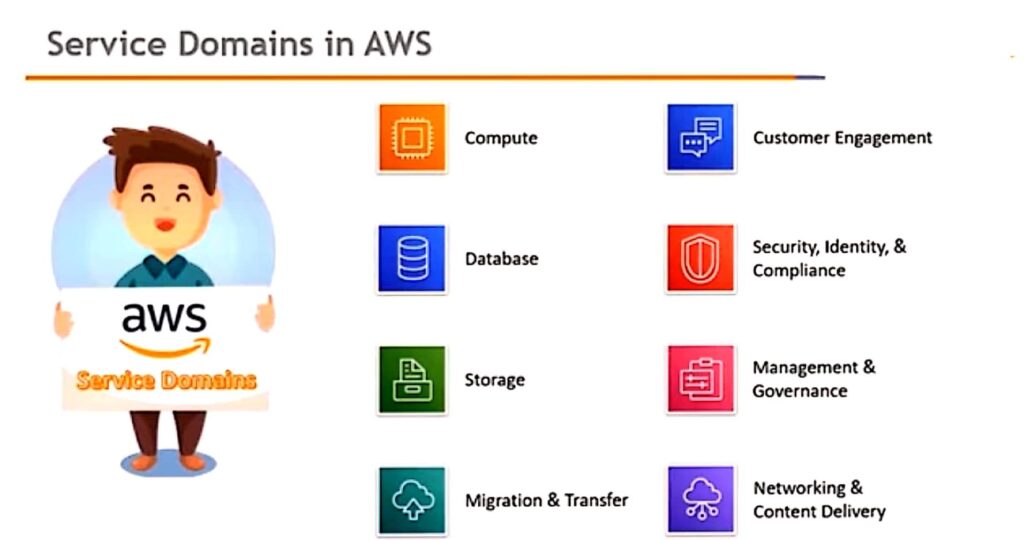
Software as a Service(SAAS)
- Salesforce:
- Salesforce “Sales Cloud” is a cloud-based Customer Relationship Management (CRM) SaaS offering.
- Salesforce “Service Cloud” is a cloud-based customer service management SaaS.
- This service cloud provides companies with a call centre like view that allows creating, tracking, routing and escalating cases.
- Salesforce “Marketing Cloud” is a cloud based social marketing SaaS offering.
- It allows companies to identify sales leads from social media, discover advocates, identify the most trending information on any topic.
- Some of the tools included in salesforce sales, service and marketing cloud are as follows: Accounts and contacts
- Leads
- Opportunities
- Campaigns
- Chatter
- Analytics and forecasts.
Software as a Service (SAAS)
This model of delivering applications, known as Software as a Service (SaaS), alleviates the burden of software maintenance for customers and simplifies development and testing for providers.
Salesforce.com, which relies on the SaaS model, offers business productivity applications (CRM) that reside completely on their servers, allowing customers to customize and access applications on demand.
An Introduction to Data Security:
Data Security
1. Data Security defines as Information in a cloud environment has much more dynamism and fluidity than information that is static on a desktop or in a network folder.
2. Nature of cloud computing dictates that data are fluid objects, accessible froma multitude of nodes and
geographic locations and, as such, must have a data security methodology that takes this into account while ensuring that this fluidity is not compromised.
3. The idea of content-centric or information-centric protection, being an inherent part of a data object is a development out of the idea of the “de-perimerization” of the enterprise.
Technologies for data security in cloud computing
Unique issues of the cloud data storage platform from a few different perspectives
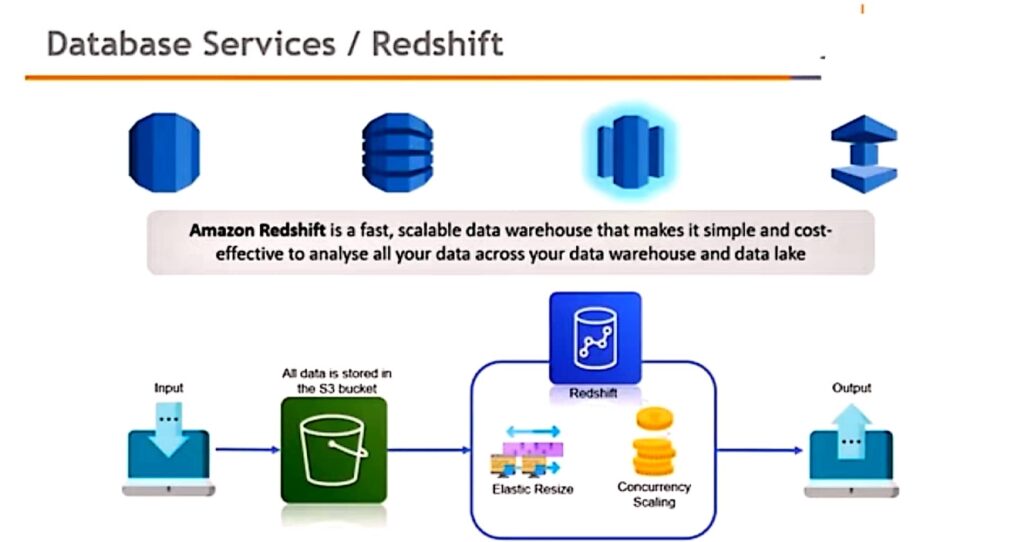
1. Database Outsourcing and Query Integrity Assurance
I. Storing data into and fetching data from devices and machines behind a cloud are essentially a novel form of database outsourcing
2. Data Integrity in Untrustworthy Storage
I. The fear of losing data or data corruption
II. Relieve the users’ fear by providing technologies that enable users to check the integrity of their data
3. Web-Application-Based Security
I. Once the dataset is stored remotely, a Web browser is one of the most convenient approaches that end users can use to access their data on remote services
II. Web security plays a more important role for cloud computing
1. Multimedia Data Security
1. The security requirements for video, audio, pictures, or images are different from other applications
Cloud computing and identity
Digital identity
1. Digital identity holds the key to flexible data security within a cloud Environment
2. A digital identity represents who we are and how we interact with others on-line.
3. Access, identity, and risk are three variables that can become inherently connected when applied to the security of data, because access and risk are directly proportional.
4. Access controlled by identifying the actor attempting the access is the most logical manner of performing this operation.
Identity, Reputation, and Trust
1. Reputation is a real-world commodity; that is a basic requirement of human-to-human relationships
2. Our basic societal communication structure is built upon the idea of reputation and trust.
User-Centric Identity:
1. Digital identities are a mechanism for identifying an individual, particularly within a cloud environment and identity ownership being placed upon the individual is known as user- centric identity
2. It allows users to consent and control how their identity (and the individual identifiers making up the identity, the claims) is used.
3. This reversal of ownership away from centrally managed identity platforms (enterprise- centric) has many advantages.
Information Card:
- Information cards are part of an identity meta-system consisting of:
- Identity providers (IdP), who provision and manage information cards with specific claims, to users.
- Users who own and utilize the cards to gain access to Web sites and other resources that support information cards.
- An identity selector/service, which is a piece of software on the user’s desktop or in the cloud that allows a user to select and manage their cards.
- Relying parties. These are the applications, services & so on, that can use an information card to authenticate a person
- And to then authorize an action such as logging onto a Web site, accessing a document, signing content, and so on.
Using Information Cards to Protect Data
1. Information cards are built around a set of open standards devised by a consortium that includes Microsoft, IBM, Novell, and so on
Cloud Computing and Data Security Risk
1. Cloud computing is a development that is meant to allow more open accessibility and easier and improved data sharing.
Data security risks are compounded by the open nature of cloud computing.
1. Access control becomes a much more fundamental issue in cloud-based systems because of the accessibility of the data
2. Information-centric access control (as opposed to access control lists) can help to balance improved accessibility with risk, by associating access rules.
3. A further area of risk associated not only with cloud computing, but also with traditional network computing, is the use of content after access.
Data-centric mashups
1. that are used to perform business processes around data creation and dissemination—by their very nature, can be used to hijack data, leaking sensitive information and/or affecting integrity of that data.
Encryption
1. It is a vital component of the protection policy, but further controls over the access of that data and on the use of the data must be met.
2. In the case of mashups, the controlling of access to data resources, can help to alleviate the security concerns by ensuring that mashup access is authenticated.
