Utility computing is a service provisioning model that offers computing resources such as hardware, software, and network bandwidth to clients when they require them on an on-demand basis.
Utility Computing
The service provider charges only as per the consumption of the services, rather than a fixed charge or a flat rate.
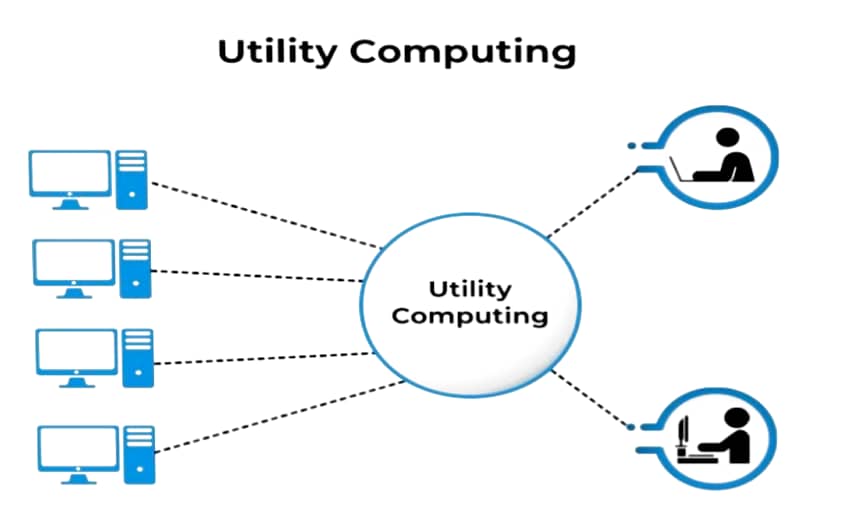
It is a fundamental concept in cloud computing that refers to the delivery of computing resources as a metered service, like utilities like electricity or water.
Also is the most trending IT service model that provides on-demand computing resources and infrastructure based on the pay-per-use method.
Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2 for web hosting, Microsoft Azure for Machine Learning, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) for data storage and backup.
Working of Utility Computing in Cloud Computing
Utility computing works on a “pay-as-you-go” model. Below is a comprehensive explanation of how utility computing in cloud computing operates:
1. Service Providers: Companies that offer utility computing services maintain vast data centers with servers, storage, and networking capabilities.
2. Customer Needs: Businesses or individual users assess their computing requirements, such as server space, processing power, or storage capacity.
3. On-Demand Access: Customers can then access these resources online, usually through a web-based interface or application programming interface (API).
4. Resource Allocation: The utility computing provider dynamically allocates resources based on the customer’s needs. This can happen almost instantly, making it easy to scale up or down.
5. Usage Monitoring: The provider tracks the resources you use, often in real time. This could be measured in data storage, processing power, bandwidth, or a combination.
6. Billing: At the end of a billing cycle, the customer is charged based on their actual usage. This avoids the cost of purchasing and maintaining in-house hardware.
7. Flexibility: As your needs change, you can easily adjust your usage, adding more resources during peak times or scaling down when less is needed.
8. Maintenance: The service provider takes care of all the backend maintenance tasks, such as software updates, security patches, and hardware upkeep, freeing you to focus on your core business
Key Features of Utility Computing
1. On-Demand Provisioning
2. Pay-as-You-Go Pricing
3. Resource Pooling
4. Measured Service
5. Scalability
Benefits of Utility Computing
1. Cost Efficiency
2. Scalability
3. Accessibility and Convenience
4. Reliability and Redundancy
5. Improved Resource Utilization
6. Rapid Deployment
7. Security
8. Global Reach
